We have the next SQL schema
And the next Stored proc to generate statistics
CREATE PROCEDURE P_GENERATE_STATISTICS
AS BEGIN
DECLARE @HighestSale INT
DECLARE @MostSoldProd INT
DECLARE @SalesAverage MONEY
SET @HighestSale =
(SELECT TOP 1 IdSale
FROM B_SALES WHERE CAST(SALEDATE AS DATE) = CAST({fn NOW()} AS DATE)
ORDER BY Price DESC)
SET @MostSoldProd =
(SELECT TOP 1 IdProduct
FROM B_SALES
WHERE CAST(SALEDATE AS DATE) = CAST({fn NOW()} AS DATE)
GROUP BY IdProduct
ORDER BY COUNT(IdProduct) DESC)
SET @SalesAverage =
(SELECT AVG(Price)
FROM B_SALES
WHERE CAST(SALEDATE AS DATE) = CAST({fn NOW()} AS DATE))
INSERT B_STATISTICS
VALUES (DEFAULT, @HighestSale, @MostSoldProd, @SalesAverage)
END
GO
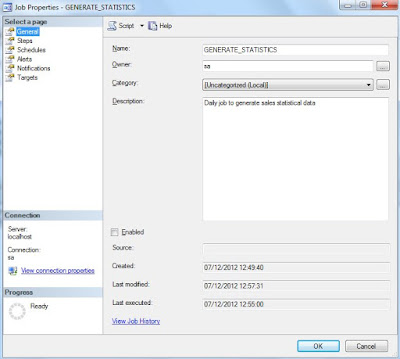
The first step to set up the Job is run the New Job Dialog at the SQL Server Agent folder. The main component of a job definition is the unique name that will be used to refer to the job
Go to the Steps tab and click New
In the Advanced tab, stablish the actions to perform in case of success and failure
In the Schedules tab, set up the triggering properties. In our case it's a recurring schedule type, with daily frequency
As a last step, we are going to set up a Notification to be sent when the Job completes with success, writing the execution information to Windows Application Event Log
The result of the Job is the next
The notification sent to Event Log can be checked through Event Viewer
<METHOD SOFTWARE © 2012>